Buying crypto doesn’t have to involve dealing with complicated exchanges. In some places, there are ATM machines designed specifically for facilitating transactions.
Guides on buying bitcoin (BTC) often start with the advice that you first need to create a cryptocurrency exchange account and download or purchase a crypto wallet to store it in. But there’s another convenient way of purchasing bitcoin that doesn’t involve using a computer, let alone a cryptocurrency exchange.
Using a bitcoin automated teller machine (ATM), people have the opportunity to purchase BTC by inserting cash or their debit cards and completing a few basic steps. But while bitcoin ATMs become a growing part of the industry, the thought of using one still strikes many as being oxymoronic.
How can something like bitcoin, which is a purely digital currency, be dispensed by an ATM that normally spits out physical currency?
It’s a perfectly good question. Here’s what you need to know.
What are bitcoin ATMs?
Bitcoin ATMs let people buy bitcoin – and sometimes other cryptocurrencies – using cash or debit cards. However, the term ATM is somewhat misleading.
Bitcoin ATMs aren’t like bank ATMs that allow customers to manage the funds in their accounts. Bitcoin ATMs are simply tools through which you can make bitcoin purchases – and sometimes sales – and do not require users to create any sort of account to do so.
Unlike cryptocurrency exchanges, bitcoin ATMs give users the option to custody their own purchased bitcoin by wiring the coins directly to a crypto wallet of their choice. However, if you use centralized exchanges like Binance or Coinbase (COIN), you can also opt to have your coins sent to your “deposit address” provided by your exchange and let the platform custody the assets for you.
Wallet creation is often a key part of the process of buying bitcoin using ATMs, and this is the part that’s usually targeted by scammers (as we’ll explore below).
The first bitcoin ATM popped up in 2013, in a cafe shop in the Canadian city of Vancouver. In those days, it was common practice among bitcoiners to spend bitcoin in cafes or drop 10,000 coins on two pizzas.
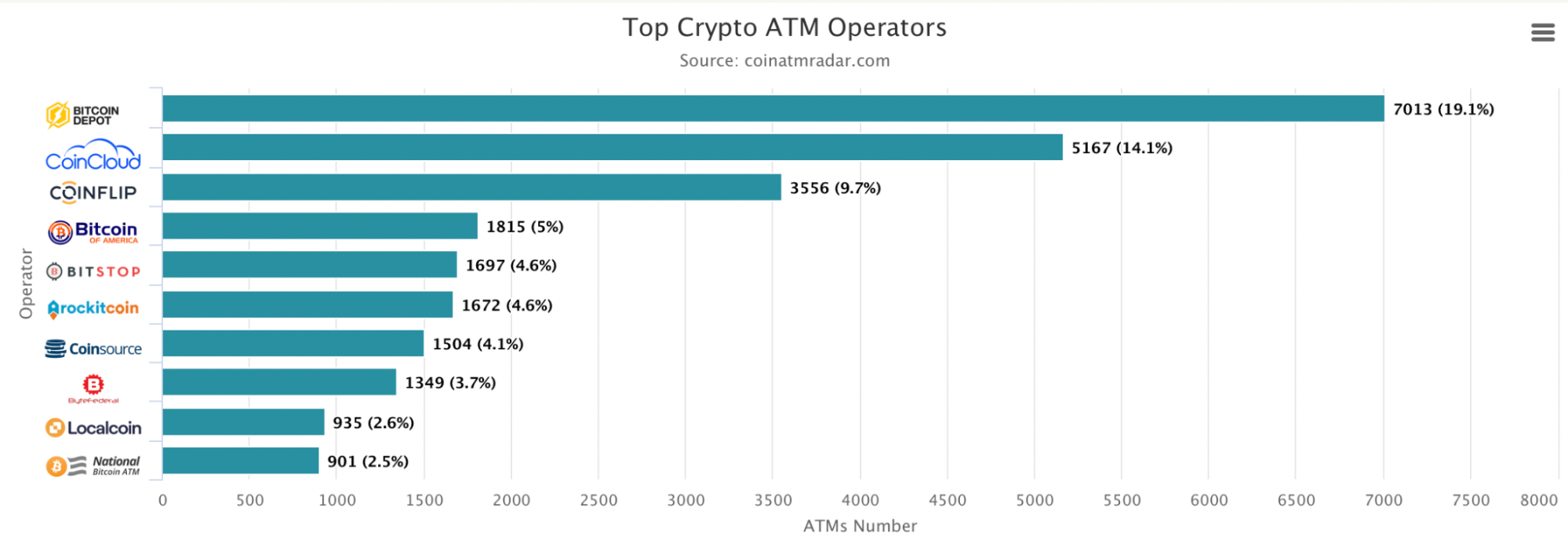
Bitcoin ATM operators (Coin ATM Radar)
Since then, bitcoin ATMs have popped up all over the world. To date, there are 36,610 bitcoin ATMs in 77 different countries, according to data from Coin ATM Radar. Genesis Coin is the largest manufacturer of bitcoin ATMs with 15,140 machines, followed by General Bytes with 7,965 and BitAccess with 5,549.
The top operators of bitcoin ATMs are Bitcoin Depot (19.1% of the market share), CoinCloud (14.1%) and CoinFlip (9.7%).
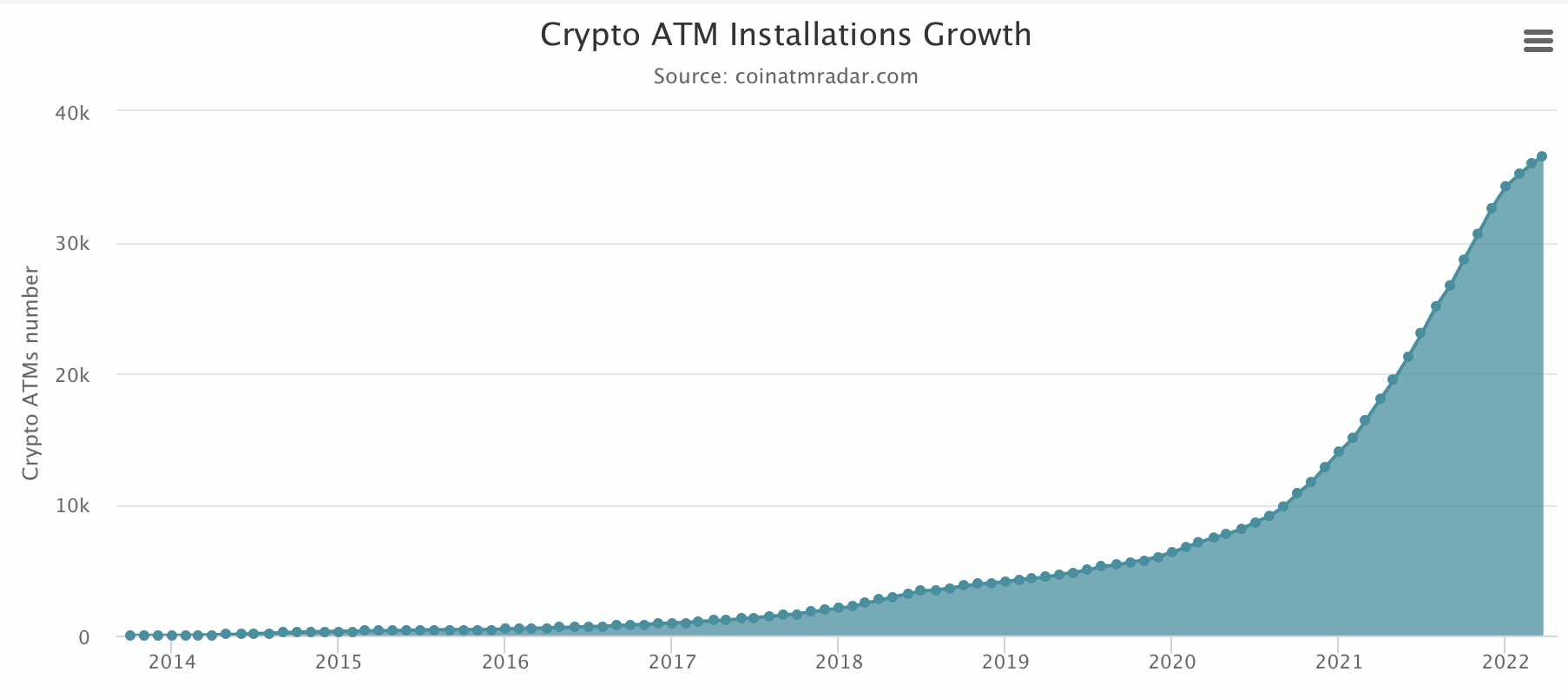
Bitcoin ATM installation growth ((Coin ATM Radar)
How to buy bitcoin from a bitcoin ATM
When you spot a bitcoin ATM, you’ll often find it has a QR code plastered on it prompting you to download a particular crypto wallet that’s supported by the ATM machine.
A popular option is the Coinbase crypto wallet, but you can choose from a long list of other wallets, too.
You’ll first need to download the wallet, if you haven’t already, and follow any setup instructions when prompted.
Your newly created wallet will generate a unique bitcoin address to which the ATM will send your purchased coins after the transaction is confirmed and completed.
Bitcoin ATMs are meant to be an intuitive experience for anyone who’s used an ATM before, so all you’ll need to do is just follow instructions on the screen.
Machines will vary somewhat depending on country and location, and some may require you to complete know-your-customer (KYC) steps before permitting the purchase. Minimum and maximum purchase amounts may also vary.
After setting up the wallet and locating your wallet address for inbound transactions, you’ll want to key in the amount you wish to purchase and enter your crypto wallet address. This is usually done automatically by scanning the QR code on your phone screen rather than typing it in manually (which can lead to mistakes and cause your funds to be lost forever.)
The transaction usually takes around 10 minutes to be completed, although it might also take as long as an hour.
Advantages and disadvantages of bitcoin ATMs
For users who aren’t tech-savvy, bitcoin ATMs are an excellent gateway into crypto. Fortunately, it doesn’t come at the cost of compromised security because most ATMs don’t store users’ KYC information, bank details or private keys.
But there are some obvious disadvantages. Bitcoin ATMs charge exorbitant fees – 7%-20% in some cases – and there are also more stringent limits on purchases compared to a cryptocurrency exchange. Also, in the event anything goes wrong, there’s little to no customer support available.
Beware of scams involving bitcoin ATMs
There are two scams that involve using bitcoin ATMs.
Scammers often advertise goods for sale on sites like eBay, Craigslist or Gumtree (UK). These items are typically priced at a significant discount to the usual market rate, luring potential buyers to get in touch.
The scammers tell victims they must make purchases via crypto if they want to secure those prices – usually by depositing funds into a bitcoin ATM and sending the crypto to the scammers’ wallet address. Once the transaction is completed, the scammers vanish.
This is popular with scammers because of the irreversible and largely unregulated nature of blockchain-based payments. Once a transaction is finalized, it’s next to impossible to reverse it.
Another type of bitcoin ATM scam is more convoluted and sinister.
Scammers often target individuals seeking employment and offer them trial work. The trial involves scammers sending money to a person’s bank account and then telling the person to withdraw it and convert the funds into bitcoin at a bitcoin ATM, then transfer the cryptocurrency to the scammers’ address.
A few days later, however, the money sent to the victim’s account is reversed because it originated from a stolen account. That leaves the victim’s account with a negative balance. (Here’s one story by a Reddit poster who was swindled out of funds this way.)
Overall, if you’re looking to purchase a reasonable amount of bitcoin in a relatively private manner and you’re not particularly bothered about paying high fees, then a bitcoin ATM could be a good choice for you – provided there are machines in your area, of course. Otherwise, using an exchange or purchasing bitcoin through apps you most likely already have on your smartphone are also good options.

















